Mind mapping engages both the logical and creative sides of the brain. It encourages brainstorming, critical thinking, and organization of ideas, which can improve memory retention and enhance creativity.

Brain Exercises: Mental exercises can be used to boost memory and creativity in students, using a combination of mindfulness practices and techniques that enhance both cognitive function and creativity. Here are 9 brain exercises designed to improve these skills:
Table of Contents
9 Brain Exercises
1. Mind Mapping
2. Chunking
3. Visualization
4. Memory Palace (Losi’s Method)
5. Creative writing and journaling
6. Brain Games and Puzzles
7. Memory Aids
8. Meditation and Mindfulness
9 Brain Exercises
1. Mind Mapping
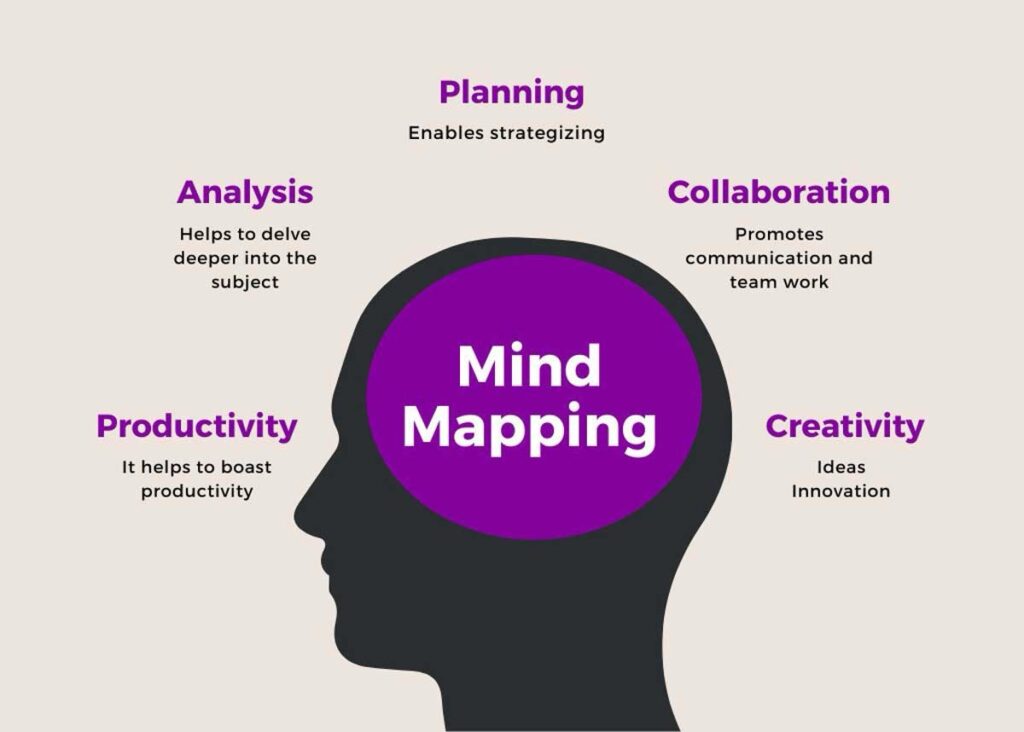
What it is: A visual tool that helps students organize information, ideas, or concepts in a non-linear way by creating diagrams with branches connecting related ideas.
How it helps: Mind mapping engages both the logical and creative sides of the brain. It encourages brainstorming, critical thinking, and organization of ideas, which can improve memory retention and enhance creativity.
How to practice: Start with a central idea, then move on to make connections.
2. Chunking
What it is: Chunking is the practice of breaking large pieces of information into smaller, manageable pieces.
How it helps: It enhances short-term memory by making complex information easier to recall. By organizing data into patterns or groups, students can remember and retrieve information more effectively.
How to practice: When studying, group related facts, vocabulary words, or concepts together instead of trying to remember everything at once.
3. Visualization

What it is: A brain exercise in which students imagine vivid images or scenarios related to the material being learned.
How it helps: Visualization stimulates the creative and memory centers of the brain. By creating mental pictures, students can increase their ability to recall information and generate new ideas.
How to practice: Encourage students to create mental images of concepts, historical events, or stories from their studies to make the material more memorable.
4. Memory Palace (Losi’s Method)
What it is: An ancient memory technique in which students mentally place the information they need to remember in specific locations within a familiar location, such as a home or on the street.
How it helps: The Method of Loci uses spatial memory to help students recall information by visualizing it in specific, familiar locations. This method is especially useful for remembering lists or sequences.
How to practice: Imagine a familiar place (such as your home) and imagine that there are objects or concepts placed in different rooms or areas that you need to remember. Afterwards, mentally visit that location to retrieve the information.
5. Creative writing and journaling

What it is: A writing practice that involves expressing thoughts, ideas, and experiences freely in a journal or through creative writing exercises.
How it helps: Writing stimulates creativity, improves linguistic skills, and helps students process ideas more clearly. It encourages imaginative thinking and helps organise thoughts, improving both memory and creativity.
How to practice: Set aside 10-15 minutes a day for creative writing or journaling. Students can write short stories, poems, or simply reflect on their day.
6. Brain Games and Puzzles
What it is: Engaging in puzzles like Sudoku, crosswords, chess or logic problems.
How it helps: Brain games challenge the brain to think in new ways, improve problem-solving skills, and stimulate areas of the brain associated with memory and creativity. They promote critical thinking in the short term.
How to practice: Combine regular practice with brain-stimulating games or puzzles. These activities can be done during breaks or as part of the daily routine.
7. Memory Aids
What it is: Memory aids that use associations, abbreviations, rhymes, or songs to help remember information.
How it helps: Memory aids take advantage of creativity by creating memorable and often amusing associations. These techniques enhance both recall and long-term memory retention.
How to practice: Create acronyms or rhymes to remember difficult concepts. For example, sequences of operations in mathematics Use “PEMDAS” to remember (parentheses, exponents, multiplication, division, addition, subtraction).
8. Meditation and Mindfulness

What it is: Meditation involves focusing attention, while mindfulness is the practice of being completely present in the moment without judgment.
How it helps: Regular meditation and mindfulness practices help improve focus, reduce stress, and enhance memory. They also stimulate creative thinking by silencing mental distractions and allowing the brain to process information more effectively.
How to practice: Spend 5-10 minutes daily in a meditation or mindfulness practice, focusing on breathing or observing thoughts without attachment.
Disclaimer: This content, including advice, provides general information only. It is in no way a substitute for qualified medical opinion. Always consult a specialist or your doctor for more information. NEWSNOW24x7 does not claim responsibility for this information.

